how to find upper and lower bounds
One to one maths interventions built for GCSE success
Weekly online one to one GCSE maths revision lessons available in the spring term
Find out more
This topic is relevant for:

Upper and Lower Bounds
Here we will learn about upper and lower bounds including how to find upper and lower bounds and how to use them to solve problems.
There are also upper and lower bounds worksheets based on Edexcel, AQA and OCR exam questions, along with further guidance on where to go next if you're still stuck.
What are upper and lower bounds?
Upper and lower bounds are the maximum and minimum values that a number could have been before it was rounded. They can also be called limits of accuracy.
The upper and lower bounds can be written using error intervals
E.g.
A rectangle has a width of
Let's look at the length:
The smallest number that will round up to give
The largest number that will round down to give 6.4 is 6.44999… so we say that
Therefore we can write:
\[ 6.35 \mathrm{~cm} \leq l<6.45 \mathrm{~cm} \]
Let's look at the width:
The smallest number that will round up to
The largest number that will round down to give 4.3 is 4.34999… so we say that
Therefore we can write
\[ 4.25 \mathrm{~cm} \leq w<4.35 \mathrm{~cm} \]
We use
These upper and lower bounds of the length and width can then be used to find the upper and lower bounds of the perimeter and area of the rectangle.
What are upper and lower bounds?

How to find upper and lower bounds
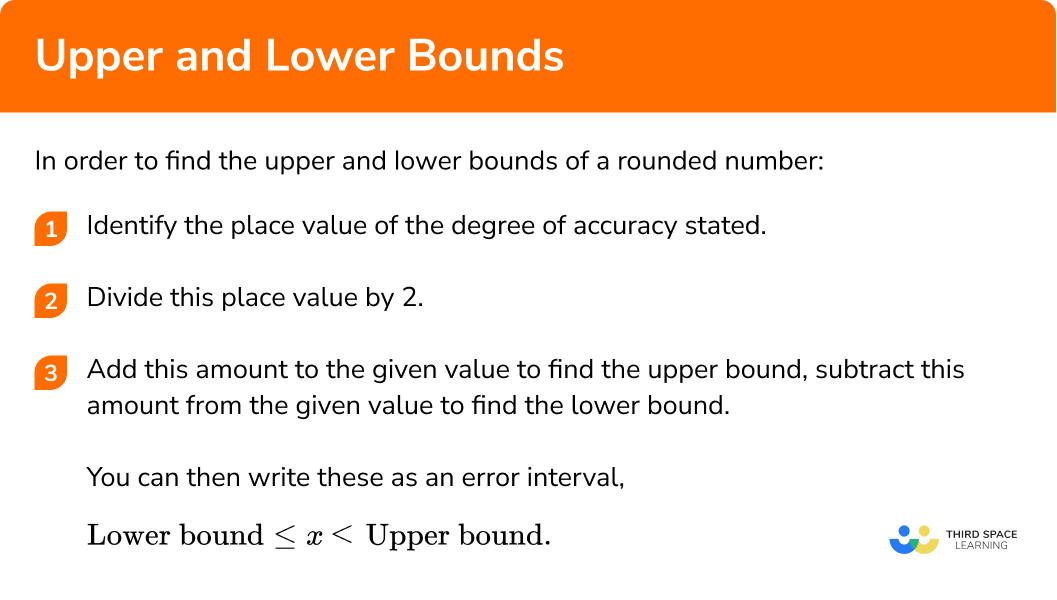
In order to find the upper and lower bounds of a rounded number:
- Identify the place value of the degree of accuracy stated.
- Divide this place value by
2 . - Add this amount to the given value to find the upper bound, subtract this amount from the given value to find the lower bound.
You can then write these as an error interval,
\[ \text{Lower bound} \leq x < \text{Upper bound} \]
Explain how to find the upper and lower bounds of a rounded number in 3 steps

Upper and lower bounds worksheet

Get your free upper and lower bounds worksheet of 20+ questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.
DOWNLOAD FREE

Upper and lower bounds worksheet

Get your free upper and lower bounds worksheet of 20+ questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.
DOWNLOAD FREE
Upper and lower bound examples
Example 1: finding upper and lower bounds
A number was given as
- Identify the place value of the degree of accuracy stated.
The place value of the degree of accuracy is
2 Divide this place value by
\[0.1 ÷ 2 = 0.05\]
3 Add this amount to the given value to find the upper bound, subtract this amount from the given value to find the lower bound.
\[ \text{Lower bound} \leq x < \text{Upper bound} \]
Upper bound
Lower bound
\[ \text{Error interval: } 38.55\leq y< 38.65 \]
Example 2: finding upper and lower bounds
The population of a town,
Identify the place value of the degree of accuracy stated
The place value of the degree of accuracy is
Divide this place value by 2.
Add this amount to the given value to find the upper bound, subtract this amount from the given value to find the lower bound.
\[\text{Lower bound} \leq x < \text{Upper bound}\]
Upper bound
Lower bound
\[ \text{Error interval: } 275000\leq y< 285000 \]
How to use upper and lower bounds in calculations
In order to use the upper and lower bounds in calculations:
- Find the error intervals of the rounded numbers.
- If adding or multiplying – group together corresponding bounds, if subtracting or dividing – group together opposite bounds.
\begin{aligned} \text{Addition: } X_{LB}+Y_{LB}\leq X+Y < X_{UB}+Y_{UB} \\\\ \text{Multiplication: } X_{LB} \times Y_{LB}\leq X \times Y < X_{UB} \times Y_{UB} \\\\ \text{Subtraction: } X_{LB}-Y_{UB}\leq X-Y < X_{UB}-Y_{LB} \\\\ \text{Division: } X_{LB} \div Y_{UB}\leq X \div Y < X_{UB} \div Y_{LB} \end{aligned}
3 Perform the required calculation and write an error interval if required.
Calculations with upper and lower bound examples
Example 3: using upper and lower bounds in an addition
A rectangle has a width
Find the error intervals of the rounded measurements.
The error interval of the width,
\[2.5\mathrm{~cm} \leq w < 3.5\mathrm{~cm}\]
The error interval of the length,
\[8.55\mathrm{~cm} \leq l < 8.65\mathrm{~cm}\]
If adding or multiplying – group together corresponding bounds, if subtracting or dividing – group together opposite bounds.
For an addition, group together corresponding bounds.
\[ X_{LB}+Y_{LB}\leq X+Y < X_{UB}+Y_{UB} \]
By adding the lower bounds for the sides, we find the lower bound for the perimeter.
By adding the upper bounds for the sides, we find the upper bound for the perimeter.
For the perimeter of the rectangle, this becomes:
\begin{aligned} 2 \left ( w_{LB} + l_{LB} \right ) &\leq P < 2 \left ( w_{UB} + l_{UB} \right )\\\\ 2 \left ( 2.5 + 8.55 \right ) &\leq P < 2 \left ( 3.5 +8.65 \right ) \end{aligned}
Perform the required calculation and write an error interval if required.
Lower bound of
Upper bound of
Example 4: using upper and lower bounds in a multiplication
A parallelogram has a base
Find the error intervals of the rounded measurements.
The error interval of the base,
\[5.635 \mathrm{~m} \leq b < 5.645 \mathrm{~m}\]
The error interval of the perpendicular height,
\[2.25 \mathrm{~m} \leq h < 2.35 \mathrm{~m}\]
If adding or multiplying – group together corresponding bounds, if subtracting or dividing – group together opposite bounds.
For a multiplication, group together corresponding bounds.
\[X_{LB} \times Y_{LB}\leq X \times Y < X_{UB} \times Y_{UB}\]
By multiplying the lower bounds, we find the lower bound for the area.
By multiplying the upper bounds, we find the upper bound for the area.
For the area of the parallelogram, this becomes:
\begin{aligned} b_{LB} \times h_{LB} & \leq A < b_{UB} \times h_{UB} \\\\ 5.635 \times 2.25 & \leq A < 5.645 \times 2.35 \end{aligned}
Perform the required calculation and write an error interval if required.
Lower bound of
Upper bound of
Example 5: using upper and lower bounds in a subtraction
A plank of wood is
Find the error intervals of the rounded measurements.
The error interval of the plank, is
\[2.995 \mathrm{~m} \leq \text{plank} < 3.005 \mathrm{~m}\]
The error interval of the cut section is
\[1.195 \mathrm{~m} \leq \text{cut section} < 1.205 \mathrm{~m}\]
If adding or multiplying – group together corresponding bounds, if subtracting or dividing – group together opposite bounds.
For a subtraction, group together opposite bounds.
\[X_{LB}-Y_{UB}\leq X-Y < X_{UB}-Y_{LB}\]
To find the lower bound of the remaining piece of wood we need to start with the lower bound of the plank and subtract the upper bound of the cut section. This will make the answer as small as possible.
To find the upper bound for the remaining piece of wood we start with the upper bound for the plank and subtract the lower bound for the cut section. This will make the answer as big as possible.
For the length of the remaining wood, this becomes:
\begin{aligned} \text{plank}_{LB} – \text{cut section}_{UB} &\leq x < \text{plank}_{UB} – \text{cut section}_{LB} \\\\ 2.995-1.205 &\leq x < 3.005-1.195 \end{aligned}
Perform the required calculation and write an error interval if required.
Lower bound of
Upper bound of
\[\text{Error interval: } 1.79 \mathrm{~m} \leq x < 1.81\mathrm{~m}\]
Example 6: using upper and lower bounds in a division
A car travels
Find the error intervals of the rounded measurements.
The error interval of the distance, is
\[615\mathrm{~km} \leq \text{distance} < 625\mathrm{~km}\]
The error interval of the time is
\[8.35 \text{ hours} \leq \text{time} <8.45 \text{ hours}\]
If adding or multiplying – group together corresponding bounds, if subtracting or dividing – group together opposite bounds.
For a division, group together opposite bounds.
\[X_{LB} \div Y_{UB}\leq X \div Y < X_{UB} \div Y_{LB}\]
To find the lower bound of the speed we need to start with the lower bound of the distance and divide by the upper bound of the time. This is because if you divide a bigger number, you are left with a smaller answer.
To find the upper bound for the speed, we start with the upper bound for the distance and divide by the lower bound for the time. This will leave us with a bigger answer.
For the average speed of the car, this becomes:
\begin{aligned} \text{distance}_{LB} \div \text{time}_{UB} &\leq \text{speed} < \text{distance}_{UB} – \text{time}_{LB} \\\\ 615 \div 8.45 &\leq \text{speed} < 625 \div 8.35 \end{aligned}
Perform the required calculation and write an error interval if required.
Lower bound of the average speed
Upper bound of the average speed
Example 7: using upper and lower bounds to find a suitable degree of accuracy
The mass
Find the error intervals of the rounded measurements.
The error interval of the mass, is
\[52.5\mathrm{~kg} \leq m < 53.5\mathrm{~kg}\]
The error interval of the volume is
\[0.0255\mathrm{~m}^{3} \leq v < 0.0265\mathrm{~m}^{3}\]
If adding or multiplying – group together corresponding bounds, if subtracting or dividing – group together opposite bounds.
For a division, group together opposite bounds.
\[X_{LB} \div Y_{UB}\leq X \div Y < X_{UB} \div Y_{LB}\]
For the density of the rock, this becomes:
\begin{aligned} \text{mass}_{LB} \div \text{volume}_{UB} &\leq d < \text{mass}_{UB} \div \text{volume}_{LB} \\\\ 52.5 \div 0.0265 &\leq d < 53.5 \div 0.0255 \end{aligned}
Perform the required calculation and write an error interval if required.
Lower bound of the density
Upper bound of the density
Both bounds round to 2000, therefore the density of the rock is
Common misconceptions
- Upper bound is incorrect
It is very common for students to put an incorrect upper bound
E.g.
If a length has been rounded to56 cm to the nearestcm , an error maybe to write the upper bound as56.4 cm .
The upper bound must be bigger than56.4 cm as56.49 also rounds down to56 , so does56.499999999 ….
The upper bound in this case is56.5 cm .
Practice upper and lower bound questions
Upper bound = 92.49 cm , lower bound = 91.49 cm

Upper bound = 93 cm , lower bound = 91 cm

Upper bound = 92.5 cm , lower bound = 91.5 cm

Upper bound = 92.55 cm , lower bound = 91.55 cm

The degree of accuracy is the units. We can divide this place value by two; add to the given measure for the upper bound and subtract from the given measure for the lower bound.




The degree of accuracy is the hundreds. We can divide this place value by two; add to the given measure for the upper bound and subtract from the given measure for the lower bound.
Upper bound = 42.94 cm , lower bound = 42.75 cm

Upper bound = 42.8 cm , lower bound = 42.9 cm

Upper bound = 42.9 cm , lower bound = 42.7cm

Upper bound = 42 cm , lower bound = 43 cm

The error interval of the height, h , is
21.35 cm \leq h < 21.45 cm
By adding the lower bounds for the height, we find the lower bound for the combined height.
By adding the upper bounds for the height, we find the upper bound for the combined height.
Upper bound = 17.85 cm^2 , lower bound = 12.35 cm^2

Upper bound = 15 cm^2 , lower bound = 10 cm^2

Upper bound = 17.875 cm^2 , lower bound = 12.375 cm^2

Upper bound = 17.8 cm^2 , lower bound = 12.3 cm^2

The error interval of the base, b , is
5.5 cm \leq b < 6.5 cm
The error interval of the height, h , is
4.5 cm \leq h < 5.5 cm
By using the lower bounds for the base and height, we find the lower bound for the area.
By using the upper bounds for the base and height, we find the upper bound for the area.
Upper bound = \pounds 15 , lower bound = \pounds 6

Upper bound = \pounds 21.50 , lower bound = \pounds 10.50

Upper bound = \pounds 16 , lower bound = \pounds 6

Upper bound = \pounds 20.50 , lower bound = \pounds 11.50

The error interval of the starting amount, P , is
£45 \leq P < £55
The error interval of the money spent, S , is
£33.50 \leq S < £34.50
For the upper bound of money remaining, we subtract the lower bound of S from the upper bound of P .
For the lower bound of money remaining, we subtract the upper bound of S from the lower bound of P .




Upper bound = 2.447 hours (3 d.p.), lower bound = 2.410 hours (3 d.p.).
Both round to 2.4 to 2 s.f., therefore, the journey took 2.4 hours.
Upper and lower bounds GCSE questions
1. The weight, w of a parcel is recorded as 440g to the nearest 10g . Write down the error interval for the weight of the parcel.
(2 Marks)
Show answer
Lower bound 435g , Upper bound 445g
(1)
435g \leq w < 445g 1 mark
(1)
2. (a) A set of books each have a width x of 1.4cm to the nearest mm . Write down the error interval for the width of one book.
(b) Kevin's bookshelf has a length of 36cm to the nearest cm . Calculate the maximum number of these books that Kevin can fit on his shelf.
(5 Marks)
Show answer
(a)
Lower bound 1.35cm , upper bound 1.45cm
(1)
1.35cm \leq x < 1.45cm 1 mark
(1)
(b)
Upper bound of shelf 36.5cm
(1)
Maximum number of books:
36.5 \div 1.35 = 27.03 1 mark
(1)
Maximum number of books is 27 .
(1)
3. A room has a width of 4.55m correct to 2 dp and a length of 3.984m correct to 3 d.p.
By considering bounds, find the area of the room to a suitable degree of accuracy.
(5 Marks)
Show answer
Lower bound of width 4.545m , upper bound of width 4.555m
(1)
Lower bound of length 3.9835m , upper bound of length 3.9845m
(1)
Lower bound of area:
4.545 \times 3.9835 = 18.1050 1 mark
(1)
Upper bound of area:
4.555 \times 3.9845 = 18.1494 1 mark
(1)
Area is:
18.1m^{2} 1 mark
(1)
Learning checklist
You have now learned how to:
- apply and interpret limits of accuracy when rounding
- find upper and lower bounds of rounded values
Still stuck?
Prepare your KS4 students for maths GCSEs success with Third Space Learning. Weekly online one to one GCSE maths revision lessons delivered by expert maths tutors.

Find out more about our GCSE maths revision programme.
We use essential and non-essential cookies to improve the experience on our website. Please read our Cookies Policy for information on how we use cookies and how to manage or change your cookie settings.Accept
how to find upper and lower bounds
Source: https://thirdspacelearning.com/gcse-maths/number/upper-and-lower-bounds/
Posted by: connersooking.blogspot.com

0 Response to "how to find upper and lower bounds"
Post a Comment